What is ECG (Electrocardiogram)
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) means recording of electrical activity of the heart. Small electrical impulses are created in the heart by so called pacemaker cells. These impulses spread through the heart muscle and make it contract. ECG records these signals as they travel through the heart. To the trained specialists, ECG provides large amount of information about the structure and the function of the heart.
In most cases ECG is measured from the skin surface with ECG electrodes. These electrodes detect very small electrical changes on the skin that comes from the heart as it contracts.
ECG is widely used to detect various abnormalities in heart rhythm, size of the heart chambers or possible damage to the heart muscle or its nervous system.
In most cases ECG is measured from the skin surface with ECG electrodes. These electrodes detect very small electrical changes on the skin that comes from the heart as it contracts.
ECG is widely used to detect various abnormalities in heart rhythm, size of the heart chambers or possible damage to the heart muscle or its nervous system.
About HRV
What are Heart Rate Variability (HRV) and Autonomic Nervous System (ANS), and why they are so important for us?
Key to the whole discussion of fostering and maintaining good health is the interaction of mind and body. Especially the interaction between the mind and the all-important physical organ, the heart. As you probably know, your body reacts to nearly everything happening around you through your emotions, observations, thoughts and activity. Your brain guides the body by regulating heart and other organs through the autonomic nervous system (ANS). There are two different branches in the autonomic nervous system, Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) and Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS), which work contrarily. The sympathetic nervous system can be described as the gas pedal of the human body, and contrarily, the parasympathetic nervous system is the break that is activated during relaxation and regeneration. A properly functioning PSNS is essential for your health as a strong PSNS facilitates regeneration and has anti-inflammatory effects.
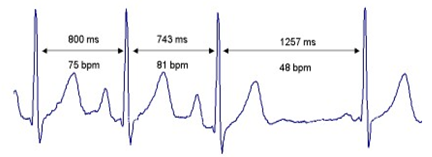
You probably are wondering how it is then possible to measure the functioning of PSNS and keep track of your own health and well-being? To fully understand this, it is also important to understand the term and concept of Heart Rate Variability. Many times we tend to assume that the interval between two heartbeats is the same, regardless of how fast or slow the heart is beating. However, a fact is that the time interval between heartbeats is all but regular, but that does not mean we are suffering from arrhythmia or other heart problems. The physiological variation of heart rate, controlled by autonomic nervous system, is called Heart Rate Variability (also commonly known as HRV). As a matter of fact this irregularity of cardiac activity, in other words Heart Rate Variability, is normal and very healthy. The more you have variation in your heartbeats, the stronger your inner brake (the parasympathetic nervous system) is.
You probably are wondering how it is then possible to measure the functioning of PSNS and keep track of your own health and well-being? To fully understand this, it is also important to understand the term and concept of Heart Rate Variability. Many times we tend to assume that the interval between two heartbeats is the same, regardless of how fast or slow the heart is beating. However, a fact is that the time interval between heartbeats is all but regular, but that does not mean we are suffering from arrhythmia or other heart problems. The physiological variation of heart rate, controlled by autonomic nervous system, is called Heart Rate Variability (also commonly known as HRV). As a matter of fact this irregularity of cardiac activity, in other words Heart Rate Variability, is normal and very healthy. The more you have variation in your heartbeats, the stronger your inner brake (the parasympathetic nervous system) is.
Figure 1: Heart rate variability.
Measuring heart rate variation reveals wide range of information about your body and health even while other physiological parameters, like blood pressure, are still in their normal or accepted ranges. HRV has been scientifically proved to be one of the best measures to test the ANS function. One of the most sensitive and efficient tests to do this is the one minute deep breathing test, where a person is breathing in and out deeply. When your PSNS (inner brake) is working normally, the heart rate should vary during the test in the following way: increasing heart rate during inhale and decreasing heart rate during exhale. The faster your heart rate drops during exhale, the better your inner brake is working, which of course increases your ability to manage your stress, and your immunity.
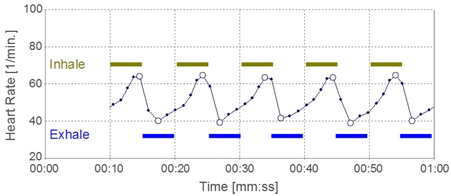
Figure 2: Heart rate curve of a healthy, athletic person (winner of multiple Olympic medals). The heart´s acceleration during inhalation and deceleration during exhalation are clearly visible, indicating a very good respiratory arrhythmia and thus an efficient parasympathetic nervous system.
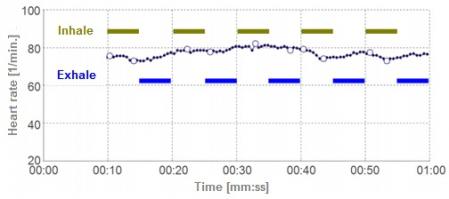
Figure 3: Heart rate curve of a person with chronically high stress levels. Despite breathing deeply, there is no respiratory arrhythmia, reflecting the weakened influence of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart.
The great fact is that despite your starting condition it is possible to improve the functioning of your ANS through different kinds of training methods, like sports or relaxation training (biofeedback training), which again increases your performance and overall well-being in the long-run. Of course in some cases lifestyle changes are needed since things like sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol will considerably weaken your PSNS. Developing a strong PSNS is also directly linked to social and emotional development: positive feelings, the ability to express emotions, healthy humor and smiling, and the ability to form and maintain healthy relationships are immensely important for the strengthening of the PSNS.