|
Application Fields
|
|
Application Field
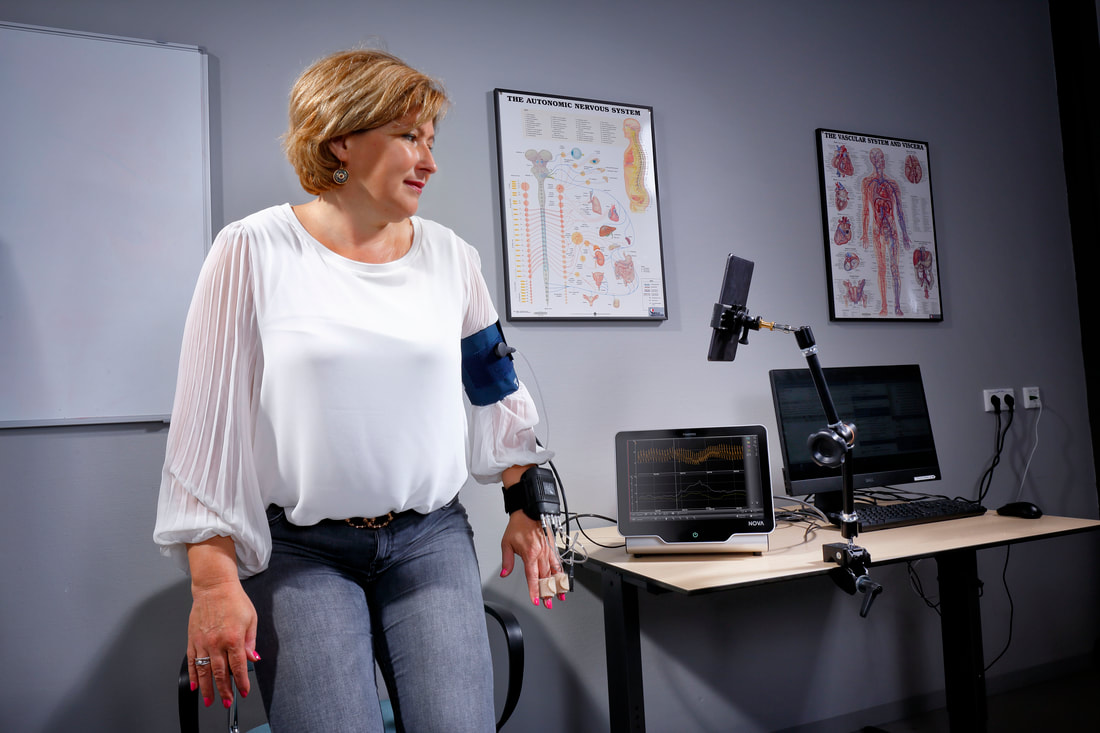
Other Application Fields Finapres® devices for continuous non-invasive blood pressure monitoring are used in many application fields. Three main fields are Autonomic failure diagnosis, Hemodynamic Evaluation, and Physiology Education. Here are a few other examples of typical Finapres® application fields! |
|
Finapres® devices in Orthostatic Hypotension
Finapres® devices have been used in the Orthostatic Hypotension research field [1-3]. The Finapres® NOVA Plus basic configuration provides accurate data to measure the effect on blood pressure of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular responses to orthostasis. Researchers have also used the Finapres® products for active stand tests [4]. The new Finapres® Guided Autonomic Testing software application facilitates several autonomic test maneuvers, including stand test! |
|
Finapres® devices in space flight & space lab research
A very special application of the Finapres® device is its use by Space Agencies like the NASA, ESA & CNES [1-3]. Especially the portable Portapres® device still provides top scientists the opportunity to do hemodynamic research on the ground, in-flight missions, and during extended stays in space. Finapres® products have been used in the former MIR station (launched 35 years ago by the Russians) and, among many others, the Dutch astronaut André Kuipers has performed physiological experiments with these devices in the currently operating NASA International Space Station (ISS). |
|
Sleep disorder research: short and long-term hemodynamic monitoring
Finapres® devices are used for sleep disorder research [8]. The newest Finapres® NOVA Plus device includes a dual finger cuff system, with cuff switching between fingers on set intervals. This permits long continuous measurements while it also allows patients to sleep comfortably throughout the night. With Finapres® devices, short and long-term hemodynamic changes will become visible on a beat-to-beat basis. This prevents losing any information between intermittent measurements, e.g. every 30 minutes, which happens when using a non-continuous monitoring device! Remote control of the Nova Plus is now included enabling the operator to control the Nova Plus from outside the sleeping patient's room. |
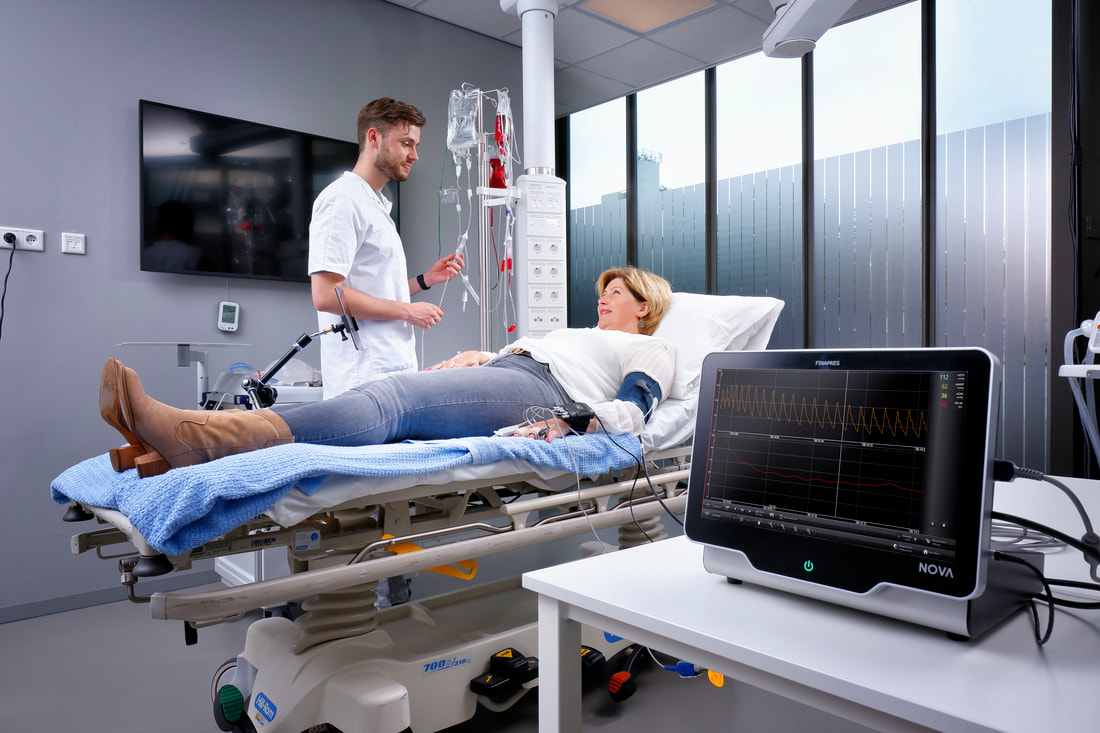
Pharmaceuticals studies using Finapres® devices
Finapres® devices are also commonly used for continuous blood pressure monitoring during clinical trials on (new) pharmaceuticals with human subjects [5-7]. Finapres® devices are able to track short and long-term hemodynamic changes beat-to-beat in a non-invasive manner during and after administration of a pharmaceutical. This is a great advantage compared to other methods such as invasive monitoring and non-continuous intermittent measurements!
Finapres® devices are also commonly used for continuous blood pressure monitoring during clinical trials on (new) pharmaceuticals with human subjects [5-7]. Finapres® devices are able to track short and long-term hemodynamic changes beat-to-beat in a non-invasive manner during and after administration of a pharmaceutical. This is a great advantage compared to other methods such as invasive monitoring and non-continuous intermittent measurements!
Drugs administration tests with Finapres® Guided Autonomic Testing (GAT) software
Our newest Guided Autonomic Testing (GAT) application facilitates seven different autonomic test maneuvers including a Drugs Administration test. This GAT application enables standardization and quantification by:
Our newest Guided Autonomic Testing (GAT) application facilitates seven different autonomic test maneuvers including a Drugs Administration test. This GAT application enables standardization and quantification by:
- supporting the operator to implement a user-defined and standardized protocol
- providing instructions to the patient
- creating an automated report with quantified results of the performed tests.
References
- O’Connor et al. “Impact of Standing Speed on the Peripheral and Central Hemodynamic Response to Orthostasis” Hypertension 2019
- Donoghue et al. “Is orthostatic hypotension and co-existing supine and seated hypertension associated with future falls in community-dwelling older adults? Results from the Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA)” PLoS ONE 2021
- Go et al. “Orthostatic Headache in Children Including Postural Tachycardia Syndrome and Orthostatic Hypotension: A Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study” Journal of Clinical Medicine 2020
- Buckley el al. “Is there an association between orthostatic hypotension and cerebral white matter hyperintensities in older people? The Irish longitudinal study on ageing” JRSM Cardiovascular Disease 2020
- Ertl, AC. et al. “Human muscle sympathetic nerve activity and plasma noradrenaline kinetics in space.” The Journal of physiology 2002
- Fu, Q. et al. “Impact of prolonged spaceflight on orthostatic tolerance during ambulation and blood pressure profiles in astronauts.” Circulation 2019
- Norsk, P. “Adaptation of the cardiovascular system to weightlessness: surprises, paradoxes and implications for deep space missions.” Acta Physiologica 2020
- Leroy, M. et al. “Short-term variability of blood pressure during sleep in snorers with or without apnea.” Hypertension 1996
- Müller, P. et al. “Angiotensin II receptor blockade with single doses of valsartan in healthy, normotensive subjects.” European journal of clinical pharmacology 1994
- Shi, S. et al. “Fludrocortisone does not prevent orthostatic hypotension in astronauts after spaceflight.” Aviation, space, and environmental medicine 2004
- Wecht, JM., et al. “Double-blinded, placebo-controlled crossover trial to determine the effects of midodrine on blood pressure during cognitive testing in persons with SCI.” Spinal cord 2020
|
|